Polymer additive refers to a kind of monomer of low molecular weight into high molecular weight of the process of polymerization of auxiliary substances added, its function is to initiate polymerization reaction, improve polymerization speed, adjust the viscosity of the system, control the branched reaction and control molecular weight, improve polymer properties and so on.
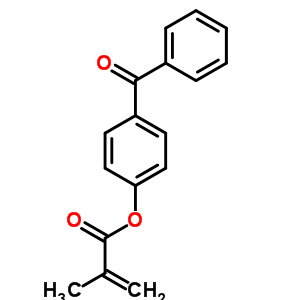
The methacrylic monomer, 4-benzoylphenyl methacrylate (BPM) was synthesized by reacting 4-hydroxy benzophenone dissolved in methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) with methacryloyl chloride in the presence of triethylamine. The homopolymer and various copolymers of BPM with glycidyl methacrylate were synthesized by free radical polymerization in MEK solution at 70 ± 1 °C using benzoyl peroxide as initiator. The homopolymer and the copolymers were characterized by FT-IR, 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopic techniques. The molecular weight ( M w and M n ) and polydispersity indices of the copolymers determined using gel permeation chromatograph suggest that the chain termination by radical recombination was predominant when the mole fraction of GMA was high in the feed. The glass transition temperature of the copolymer increases with increase in BPM content. The thermal stability of the copolymers increases with increases in BPM content. The copolymer composition was determined using 1H NMR spectra.
Reg Office: Room 435, Building 9, No.2568 Gudai Road, Minhang District, Shanghai, China.
Pilot Lab: Building 1, No. 589 Qinling Street, Shijiazhuang High-tech Zone,Hebei, China.
Plant Unit 1: Xincheng town clean chemical park, Xinji, Hebei, China.
Plant Unit 2: Dongming County South Chemical Park, Heze City, China.
Tel: +86-21-34943721
Email:Massive@massivechem.com
Info@massivechem.com
Shanghai Massive Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved(C)2023 Supported by Record number:沪ICP备18008139号